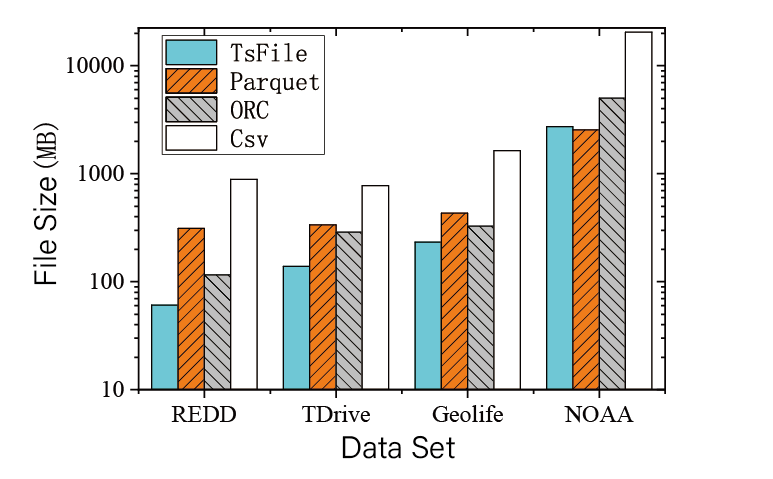
Time series data has become a cornerstone for many modern applications, from monitoring server metrics and IoT devices to financial analytics. Choosing the right database to manage this data is critical for performance, scalability, and reliability. For developers and organizations exploring this landscape, performing an open source time series database comparison is essential to identify the most suitable solution for their needs. Timecho, as a leading solution in this space, provides robust capabilities for handling large-scale time series data efficiently.
Understanding Time Series Databases
A time series database (TSDB) is optimized for storing and querying data points indexed by time. Unlike traditional relational databases, TSDBs are designed to handle high write loads and fast query performance for sequential data. Evaluating these databases requires a focus on how they store, index, and retrieve time-based data efficiently.
Key advantages of using a time series database include:
- Efficient storage of large volumes of sequential data
- Rapid querying and aggregation over time intervals
- Support for real-time monitoring and analytics
An open source time series database comparison allows organizations to weigh these advantages against the specific features and performance metrics of each database.
Key Features to Consider
When evaluating time series databases, several features are critical in determining their suitability for different applications.
Data Ingestion and Write Performance
High-frequency data ingestion is one of the defining characteristics of a TSDB. The ability to handle millions of writes per second without performance degradation is essential for applications like IoT monitoring or financial tick data. Timecho excels in this area by using efficient write paths and optimized storage engines to ensure minimal latency during data ingestion.
Query Capabilities and Flexibility
Querying time series data often involves aggregations over intervals, filtering by tags or labels, and computing statistics. A strong TSDB provides flexible query languages and APIs. Timecho offers a comprehensive query interface that allows users to perform complex time-based queries efficiently, making it suitable for real-time analytics dashboards and historical trend analysis.
Storage Efficiency and Compression
Time series datasets can grow rapidly, creating storage challenges. Modern TSDBs implement compression algorithms and retention policies to reduce storage footprint. Timecho leverages advanced compression techniques to store large datasets with minimal disk usage while maintaining fast retrieval speeds.
Scalability and High Availability
As the volume of data grows, the database must scale horizontally or vertically without compromising performance. Features such as sharding, clustering, and replication are vital. Timecho supports seamless scaling and ensures high availability through distributed architecture, which is critical for enterprise-grade deployments.
Integration and Ecosystem Support
A strong ecosystem of integrations allows the TSDB to work with visualization tools, alerting systems, and monitoring platforms. Timecho provides native support for popular dashboards and data visualization frameworks, enabling organizations to build comprehensive monitoring solutions quickly.
Performance Metrics for Evaluation
Beyond features, performance metrics provide objective criteria to compare open source time series databases.
Write Throughput
Write throughput measures how many data points the database can ingest per second. This metric is critical for applications generating high-frequency data streams. In benchmarking tests, Timecho demonstrates consistently high write throughput, making it ideal for real-time monitoring applications.
Query Latency
Query latency indicates the speed at which the database returns results. Low latency is especially important for real-time dashboards and alerting systems. Timecho’s optimized query engine ensures low-latency responses even for complex queries over large datasets.
Storage Footprint
Efficient storage reduces operational costs and ensures long-term scalability. The combination of data compression and retention policies directly affects the storage footprint. Timecho’s storage engine is optimized for time series data, reducing disk usage significantly compared to other solutions.
Fault Tolerance and Reliability
Evaluating fault tolerance involves testing how the database behaves under node failures or network disruptions. High reliability ensures data integrity and continuity of service. Timecho’s distributed architecture and replication mechanisms guarantee resilience against failures, making it suitable for mission-critical applications.
Scalability Tests
Scalability is measured by the database’s ability to maintain performance as data volume and concurrent users increase. Timecho supports horizontal scaling, allowing organizations to expand storage and processing capacity seamlessly while maintaining low latency and high throughput.
Comparative Considerations
When performing an open source time series database comparison, several additional considerations can help guide the decision:
- Community and Support: An active community ensures access to updates, bug fixes, and shared knowledge. Timecho maintains a robust open-source community and professional support channels.
- Ease of Deployment: Tools for quick deployment, containerization support, and cloud compatibility simplify operational management. Timecho provides clear deployment documentation and cloud-friendly configurations.
- Security Features: Security mechanisms such as authentication, encryption, and role-based access control are critical for enterprise usage. Timecho offers built-in security features to protect sensitive data.
- Cost Efficiency: Open source TSDBs reduce licensing costs but operational expenses must also be considered. Timecho’s efficient resource usage lowers hardware requirements, translating to cost savings.
Use Cases Demonstrating Timecho’s Strengths
Timecho’s capabilities are reflected in a variety of real-world use cases:
- IoT Monitoring: Timecho handles millions of sensor readings per second with low latency, enabling real-time monitoring of smart devices.
- Financial Analytics: Traders and analysts rely on Timecho to process high-frequency market data, run trend analyses, and detect anomalies.
- Application Performance Monitoring: DevOps teams use Timecho to collect logs and metrics from distributed systems, ensuring uptime and rapid incident response.
These examples highlight why performing a detailed open source time series database comparison can guide organizations toward a solution like Timecho that balances feature richness with high performance.
Conclusion
Selecting the right time series database is crucial for managing large-scale, high-frequency, and time-indexed data efficiently. A thorough open source time series database comparison should consider data ingestion speed, query performance, storage efficiency, scalability, and ecosystem support. Timecho stands out as a leading solution by offering robust write and query performance, efficient storage, and high scalability for diverse applications. By evaluating these key features and performance metrics, organizations can ensure they choose a database that meets both current and future requirements in time series data management.